The OpenWrt community has complied a dataset of Wireguard performance tests run (under OpenWrt, of course) on different hardware. The dataset is available here:
https://forum.openwrt.org/t/a-wireguard-comparison-db/187586
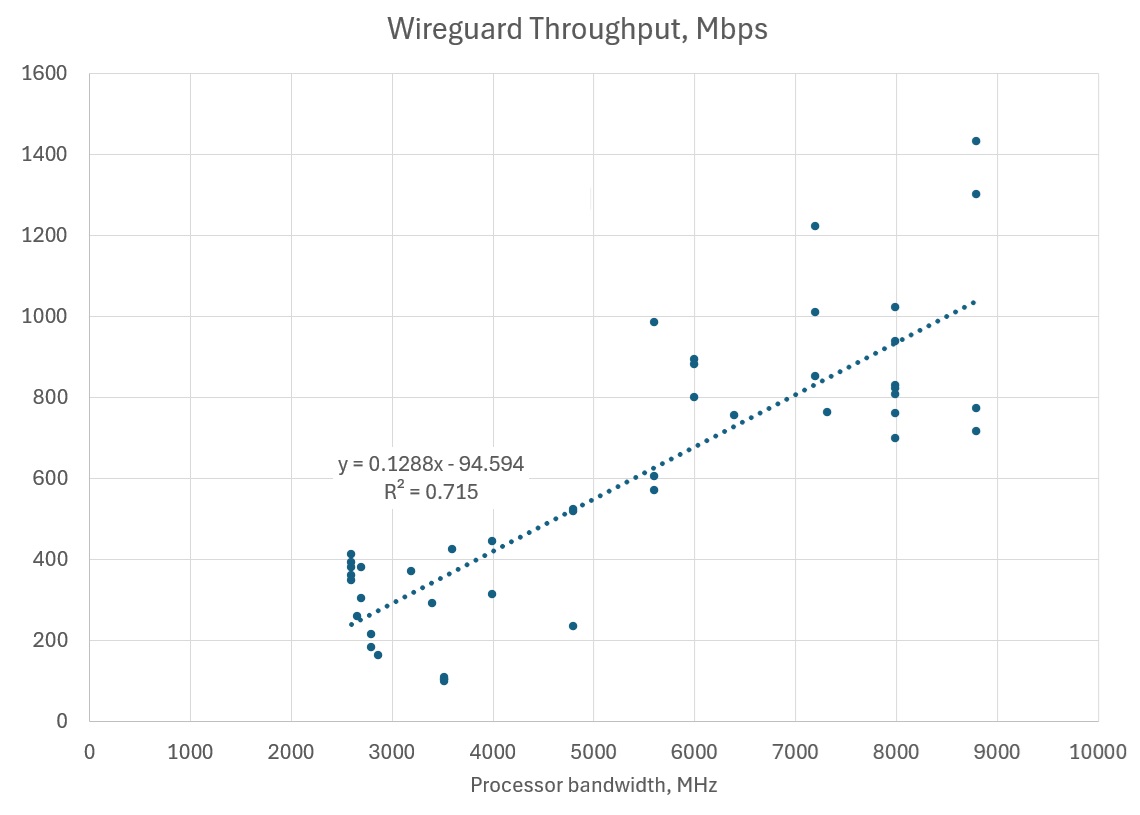
We have downloaded this dataset on June 29, 2024 (it has probably been expanded since). Then, we truncated the sample to exclude devices with processor bandwidth below 2 GHz and above 10 GHz (the idea was to produce an estimate relevant to the mid-range hardware). Next, we computed processor bandwidth (number of cores or threads, whatever is relevant, times clock speed) for each test case. Finally, we ran a simple regression model to elicit the relationship between processor bandwidth and Wireguard throughput. The model came out as follows:
T = 0.1288 B - 94.59 (R² = 0.715), where
T is measured Wireguard throughput in Mbps,
B is processor bandwidth in MHz
Note the relatively low R²; it appears to reflect differences in Wireguard implementations for different hardware platforms, as well as in cooling efficiency. Note further that newer processors are likely to have optimizations that enhance Wireguard performance significantly compared to these expectations (we actually saw this with a few N100 devices that we truncated from the sample).
The graphical representation of the model is shown below.